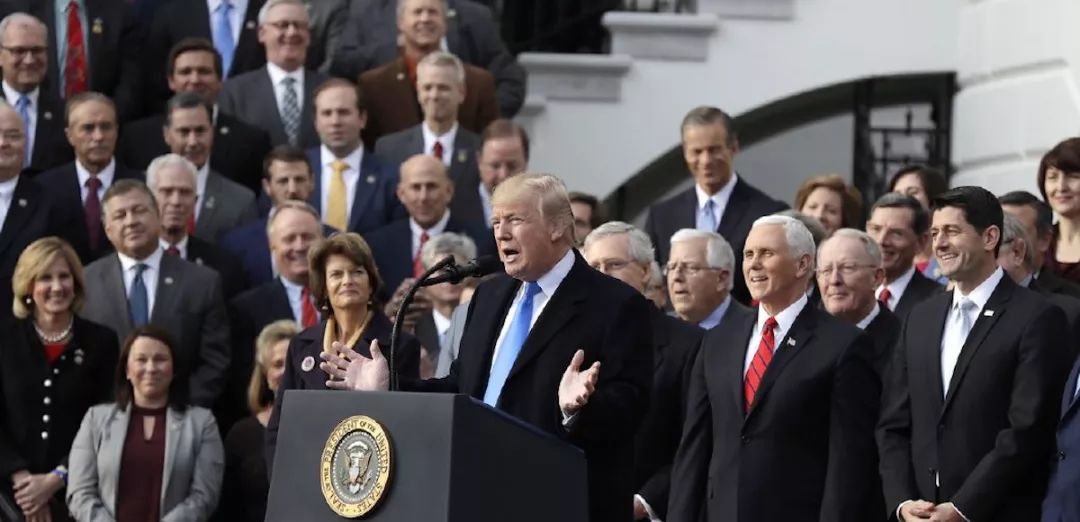

On December 22, 2017, trump signed the United States tax reduction and Employment Act, a comprehensive tax reform bill. This time, the tax reform has a wide range of contents. Once implemented, it may have a significant impact on the U.S. economy and the world economic pattern.
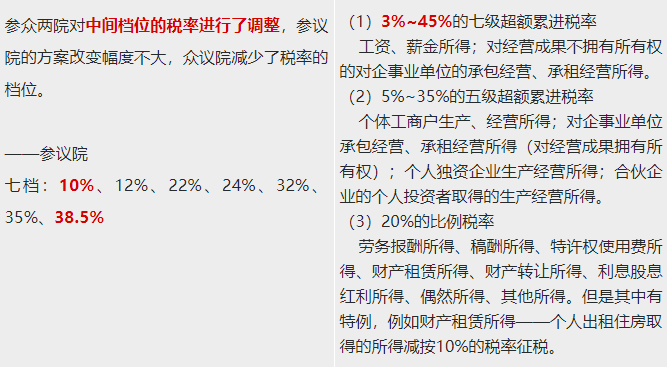
The most remarkable feature of this tax reform in the United States is the extensive and substantial tax reduction, which reduces both personal income tax and corporate income tax. The maximum tax rate of the adjusted individual income tax was reduced from 39.6% to 37%, and the minimum tax rate was reduced from 12% to 10%. At the same time, the tax exemption for individuals and families doubled to 12000 US dollars and 24000 US dollars respectively. The pace of corporate income tax cut is more radical. From 2018, corporate income tax in the United States will be permanently reduced from 35% to 21%, a one-off reduction of 14 percentage points. Small and medium-sized enterprises, such as sole proprietorship or partnership enterprises, account for about 95% of the total number of enterprises in the United States. According to the tax reform act, such enterprises are applicable to the tax rate that is more favorable than the corresponding individual income tax, and the preferential range is 20%.
Another important feature of this tax reform is that it is a more important policy adjustment than simple tax reduction. It attaches great importance to stimulating investment and attracting capital return. For example, to encourage investment, the Tax Reform Act provides that capital goods can be directly deducted without having to be depreciated in five years.
This tax reform in the United States has aroused a lot of hot discussion. The mainstream voice is talking about tax reduction. How much has it been reduced? How much is the gap with the tax provisions of our country?
corporate income tax

individual income tax
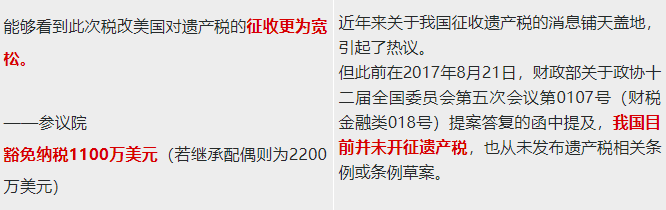
Estate duty
Net investment income tax

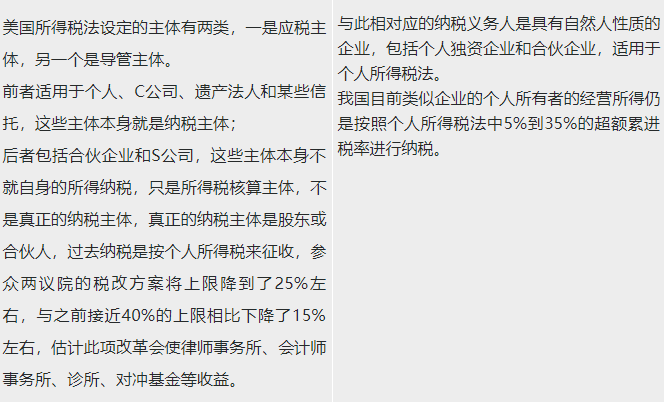
Conduit business owner
A conduit company is a company usually established for the purpose of evading or reducing taxes, transferring or accumulating profits. Such companies are only registered in the host country to meet the organizational form required by law, rather than engaging in manufacturing, distribution, management and other substantive business activities. Conduit companies in such tax avoidance arrangements are usually in the form of companies, but may also be partnerships, trusts or similar economic entities.
One time profit remittance tax
In China, if the dividend is remitted back to China in the form of dividend distribution, after receiving the dividend, the Chinese resident enterprise will revert to the pre tax income, calculate the payable Chinese enterprise income tax, and make up payment or carry forward according to the limit; if the dividend is remitted back to China in the form of interest income, the Chinese resident enterprise needs to pay in China when receiving the overseas interest, royalties and service fees Pay enterprise income tax. In the above two cases, in a simple way, they are about equal to the collection of one-off profit repatriation tax at the enterprise income tax rate.
In the US tax reform, the profits of 2.6 trillion US dollars hoarded overseas by multinational enterprises for tax avoidance can be legally remitted back to the US only by paying 14% at a time, down more than 50% compared with the previous 35%.
Global tax system
The previous global system led to the company's overseas profits being kept overseas, which may attract some profits to the United States.
In China, resident enterprises are still taxed on their worldwide income. Non resident enterprises that set up institutions and places in China and obtain income and all the actual connections between them shall be taxed on the income from sources in China and the income incurred outside China but actually connected with the institutions and places they set up in China; however, those that set up institutions and places in China and obtain income and none of the institutions and places they set up The non resident enterprises connected with each other are only taxed on the income they come from within the territory of China.
Another important feature of this tax reform is that it is a more important policy adjustment than simple tax reduction. It attaches great importance to stimulating investment and attracting capital return. For example, to encourage investment, the Tax Reform Act provides that capital goods can be directly deducted without having to be depreciated in five years.
This tax reform in the United States has aroused a lot of hot discussion. The mainstream voice is talking about tax reduction. How much has it been reduced? How much is the gap with the tax provisions of our country?
According to foreign media reports, China regards Trump's tax cut as a 'threat' and is making contingency plans, including guiding market interest rates higher, strengthening capital control and increasing the frequency of foreign exchange intervention, so as to support the RMB exchange rate and ensure that funds are not absorbed by the United States. Anonymous Chinese officials said the US tax reform plan is a 'grey rhinoceros', a new threat. Especially in the first quarter of this year, China will face several tough battles.
China's corporate tax China is one belt, one road in the world. The World Bank statistics, accounting for about 68% of the total profits of the enterprises and only 44% of the us profits, and the general decline of corporate profits, China's forced to follow up tax cuts, reduce government revenue and increase its debt. The expenditure of 'one belt, one road', Asian investment banking, arms development and social security for the elderly will inevitably weaken the financial resources of the government. China will face severe situation.
In response to tax cuts in the United States, Japan is discussing salary increases and corporate tax rates to be reduced to less than 25%. Germany also announced the reform of the tax system in January. A series of tax cuts in the United Kingdom, corporate income tax and capital gains tax have been reduced. This year, France's compulsory tax will be reduced by about 7 billion euros. India also implements a unified goods and services tax. China says it will not compete for tax cuts, but the authorities are facing a dilemma as government debt increases, decreases or does not decrease. In 2016 and 2017, China's economy is ahead of the rest of the world. Can 2018 continue to be a glorious year?
American manufacturing has been trying to keep up with the rest of the world. Higher taxes and over regulation are holding back American manufacturers. In the House Republican blueprint, two of the main corporate proposals could go a long way to many American manufacturers. The first area of interest is to reduce the corporate tax rate from 35% to 20%. At present, the tax rate of 35% is much higher than that of OECD countries. The average corporate tax rate is 24%. If U.S. manufacturers tax at nearly 24% in the future, they can greatly improve their global competitiveness. The second proposal would eliminate the current U.S. global tax system and replace it with a regional tax system. Up to now, U.S. companies have been required by law to pay taxes on foreign income in the country in which they operate, and to pay more U.S. taxes when they bring it back to the United States. Most other non-U.S. businesses use a regional tax system. This means that they can remit foreign income back home, and sometimes there is no residual domestic tax.
If the plan is adopted as envisaged today, the border adjustment will prevent us companies from deducting the cost of raw materials or finished products imported into the US.
Here's an example: 'a U.S. manufacturer who imports $800 worth of materials for products assembled in the United States and sells them for $1000 will no longer be able to deduct $800 from its revenues. This tax obligation is calculated not as the difference between the profit income of $200 and the cost of imported materials, but as a deduction from the total $1000 received for the product. In a 20% tax world, such a company would pay $200, not $40. '
Clearly, some of the proposed tax reforms could have a significant impact on US manufacturers and their global competitiveness. However, other areas of this legislation may require manufacturers to reorganize the supply chain.
As part of the extensive tax reform in the United States, the federal corporate tax rate in the United States will be reduced from 35% to 21% as of January 1, 2018.
For example, as an international non-woven company, the net deferred income tax liability of suominen group in the United States is about 10 million euros. The company's net deferred tax liabilities are expected to decrease by approximately EUR 4 million as a result of the decrease in corporate tax rates. This non recurring item will increase the profit of suominen in 2017, because the company's income tax reduction of the total income tax of the current fiscal year will be recognized in the 2017 financial statements, and there is no impact of cash flow.
With regard to the impact of the new investment on the accelerated depreciation allowance of income tax in 2017, suominen expects that the tax system reform will also have a positive impact on the company.
In a comprehensive analysis, the following tax system reform will have a greater impact on American non-woven manufacturers.
1. Reduction of enterprise tax rate:
At present, the highest corporate tax rate is 35%. The new law will reduce that to 21% (25% of personal service companies). The government and some economists expect this to kick start the economy, stimulate wage and employment growth, and encourage investment. The growth rate of foreign capital utilization in China's manufacturing industry will further slow down or even show negative growth. From January to July 2017, China's manufacturing industry actually utilized US $20.48 billion in foreign investment, down 5.7% year on year. Once the new tax reform plan is implemented, the ability of the United States to attract foreign investment will be greatly improved, which will directly weaken the ability of China's manufacturing industry to attract foreign investment, and the growth rate of foreign investment utilization will further slow down or even show negative growth.
2. The tax rate of 'transfer' business is reduced:
This allows for a deduction of 20% of the income of the sole proprietorship, limited partners and the partnership (up to 50% of the salary paid by the business). However, this ratio only applies to 'delivery' business in some industries. For example, a service-oriented 'delivery' business, such as legal or financial services, would not meet lower rates, but the non-woven manufacturing industry would be eligible.
3. Accelerate the commercial consumption of certain investments:
This allows companies to write off capital investment immediately, rather than increasing over the life of the asset. For the heavy asset non-woven manufacturing industry, this can help expand the manufacturing scale by purchasing new equipment and assets more cost-effective.
4. Reduce interest expense:
The new law limits the deduction of interest to 30% of the adjusted taxable income of the enterprise. This seems to be to curb corporate debt.
5. Retention of job tax credits and other incentives:
Earlier versions of the act attempted to repeal WoTC, allowing businesses to require that employees from specific target groups, such as veterans and snap recipients, be hired and retained for tax credits. The final act retains this credit, along with the research and development credit new market tax credit and the exemption of private activity bonds.
6. Overseas profit tax:
In order to remit the profits stored overseas, 15% tax is levied on the company's offshore cash assets and 8% tax is levied on non cash assets. In the United States, a lower one-time repatriation tax is imposed on overseas assets, and a lower tax rate is applied to non cash assets, which will encourage American enterprises to speed up the relocation of overseas factories and equipment, and China's medium and high-end manufacturing industry will inevitably be impacted.
After trump took office, he spoke to many enterprises, who would pay taxes to those who did not withdraw American production. Now some enterprises have promised to return to the United States to run factories. Over the past year, Samsung, LG, Intel and apple have successively built factories in the United States, and Haier, Hisense, Fuyao Glass and other high-end manufacturing enterprises in China have also expanded their investment in the United States.
For China, one of the representative enterprises is Cao Dewang's Fuyao Glass. What are the characteristics of Cao Dewang's investment in US factories? His market was originally in the United States, and his car glass was originally sold to General Motors and Ford. But he was originally made in China and exported to the United States. Now he built his factory in the United States and produced it in the United States. He still sells it to General Motors and Ford in the United States, and some of it may also be sold to China. His market hasn't changed, it's just changing the place of production. As soon as the place of production changes, all its costs will change. There must be a gap between some of these costs and those of China. For example, energy cost, how much does he use natural gas? How much is it in China? How much does he use electricity? How much does he use electricity in China? How much is his labor
What's the most important thing? It is the US government that is also attracting investment. He spent more than $10 million on a piece of land, not in the East, not in the west, but in the middle. This land is cheaper. Although it costs more than $10 million, the government has paid him another $17 million because he employs 1100 blue collar workers, which is equivalent to that the land has no money. This is also investment attraction. Now, it's very important for trump to succeed in his campaign to find jobs for blue collar workers.
According to Cao Dewang, all the workers he hired were workers over 40 years old without advanced skills. At present, the white-collar employment rate in the United States is very high, and the blue collar employment rate, especially the older one, is very low. Therefore, Trump's campaign plan to restore manufacturing in the United States is to solve the employment of a group of blue collar workers.
So many companies whose markets are already in the United States need to export their products to the United States. Some of them have invested and built factories in the United States, and some will also consider moving to the United States. At present, we are removing production capacity, such as steel surplus, coal and cement surplus. After the new tax reform, the non-woven enterprises, through tariff increase and trade war, are more difficult to export, and there will be a decline in demand, or even a surplus. In 2016 and 2017, the capacity is increasing, and the overcapacity of such products is not considered at all. Now, it seems that 2018 and some time in the future also need to be reexamined.